SC Cryogenic Cold Gun
Feature
- Simply supply compressed air to deliver cool air 50°C (max) cooler than the supply air
- Using the principle of eddy current centrifugation, there is no need to replace consumable parts in use, which can maintain a long service life
- Using cold air can be easily applied to local cooling operations in various industries, such as spot welding. Next. Rapid cooling during metal processing...etc
Action and Principle
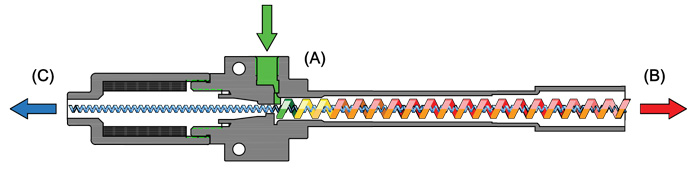
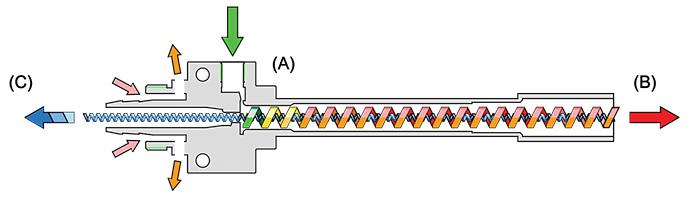
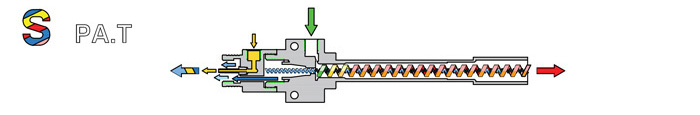
1. Action
The air cooler uses a vortex tube to generate low-temperature air. The compressed air generates a hot air flow through the vortex tube, and exchanges heat with the cold air flow, so that the hot air is discharged to the hot air outlet, and the amount of discharged air can be determined by Adjust the valve setting, and the cold air is blown out to the ( C ) cold air outlet in the direction of the arrow.
2. Principle
When the high-pressure air compressed from the air compressor enters the ( A ) vortex generator, it will expand the gas volume, resulting in
Swirl and adjust the valve direction from (A) to (B), moving in a spiral. The airflow rate near the central axis of the pipe is relatively large, and the rate near the pipe wall is relatively small. When the airflow spirals along the tube for a certain distance, the distribution of velocity with radius will become more even, because the inner air will work on the outer air due to its viscosity, so when the outer air hits the outlet of the hot air will be heated.
The airflow at the center of the vortex flows to ( C ) the cool air outlet, expands and cools as it passes through the blow inlet. Therefore, the temperature increase of the air in the outer layer of the vortex is due to the viscous work of accelerating the air flow in the outer layer, while the air in the center part flows in the opposite direction and cools down due to diffusion.
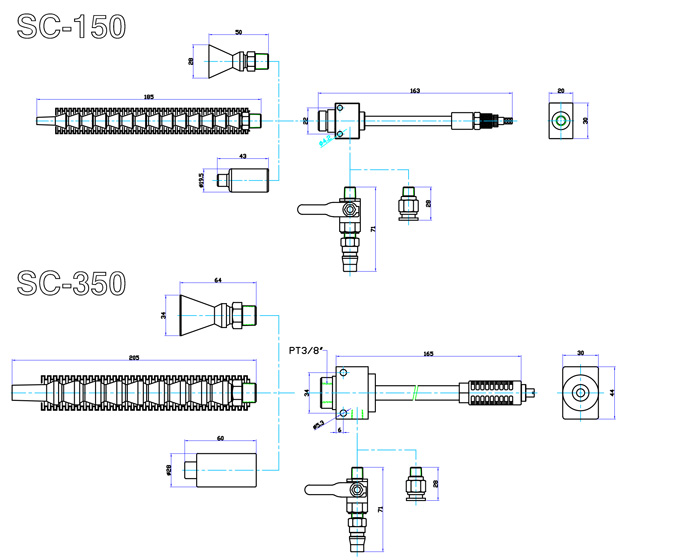
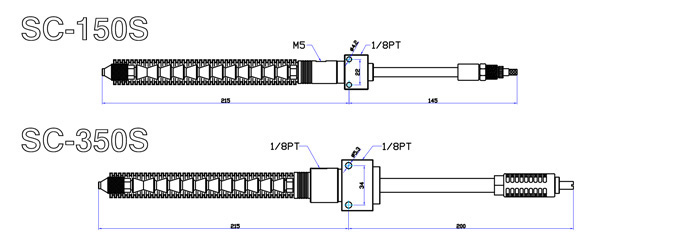
Dimensions
Main case cooler application
Local cooling of key components inside the electric control cabinet, engine control center
Cooling of computer protection center of electrical system, cooling of electronic control device of CNC machining center
Dimensions
Main case cooler application :
Local cooling of key components inside the electric control cabinet, engine control center.
Cooling of computer protection center of electrical system, cooling of electronic control device of CNC machining center.
Main case cooler selection
I. Select a category ( first step )
The main case cooler is divided into continuous working type and temperature control type. Continuous duty type: suitable for occasions requiring continuous cooling and purification
II. Main case cooler energy ( second step )
After calculating the heat load of the main casing to be cooled, the cooler with the corresponding energy can be selected.
Necessary conditions for calculating heat load ( five elements ) :
1. The current external ambient temperature; 2. The current internal temperature of the main casing ( or the total calorific value of the electronic components in the main casing ) ;
3. External ambient temperature; 4. Desired internal temperature; 5. Main case size: height, depth, width.
Calculation formula:
a. Total heat load ( Kcal/hr. ) = internal and external temperature difference coefficient ( see temperature conversion coefficient table ) X total area + internal and external temperature difference coefficient X total area of main casing ( ㎡ ) ;
b. Total heat load ( Kcal/hr. ) = total internal heat generation ( Kcal/hr. ) + internal and external temperature difference coefficient X total area of main casing ( ㎡ ) .
Note: The total area of the main case does not include the area of the top and bottom of the main case 1W=0.86Kcal/hr.
III. Example:
1. If the size of a main case is: height 180CM, depth 60CM, width 180CM
2. The current external ambient temperature: 35°C, the external ambient temperature: 40°C, the internal temperature of the main case: 40°C, and the desired temperature is 25°C
3. Total area = 1.8 X 1.8 X 2 + 1.8 X 0.6 X 2 = 8.64 ㎡
4. Internal and external temperature difference = 40°C ( internal temperature of main case ) -35°C ( current external ambient temperature ) = 5°C
5. Internal and external temperature difference = 40°C ( outside ambient temperature ) -25°C ( desired temperature ) = 15°C
6. Total heat load = total area 8.64㎡ X 9.7 ( the coefficient when the temperature difference is 5 ) + 8.64 X 27 ( the coefficient when the temperature difference is 15 ) = 317Kcal/hr.
7. From this, we should recommend a main case cooler with a cooling capacity of 428 Kcal/hr.
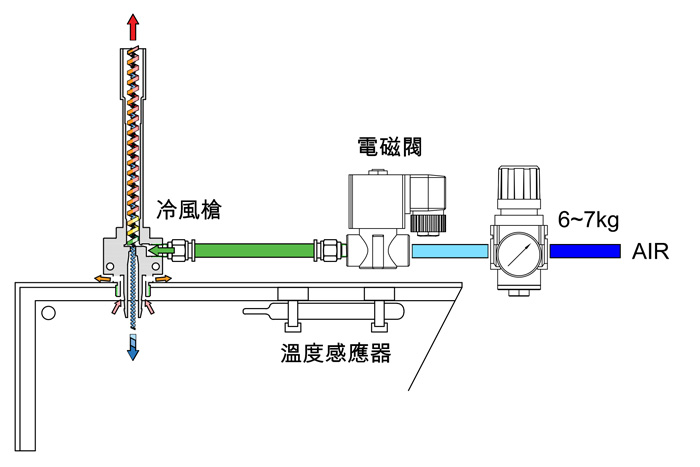
The cold air gun is used with MQL to cool and lubricate the tool processing, the local low temperature is formed in the cutting area, and the mechanical properties of the processed object and the processing tool change in this state, making it beneficial to machining, especially for some difficult-to-machine materials, such as titanium alloys , alloy steel, low carbon mild steel and some composite materials with particularly strong plasticity and toughness, etc., to form a better processing state
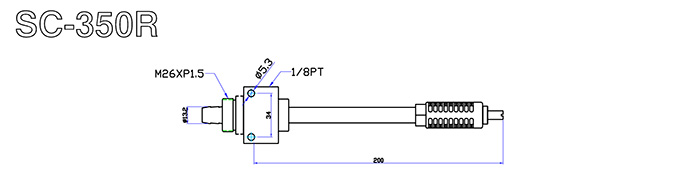
Dimensions
Cold air efficiency table
SC-150
| Cold air ratio % |
Inlet air ( inlet air 16°C ) | Spit out cold air volume | Intake air / cold air | Hot air | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure kgf/cm² |
Air volume l/min |
Air volume l/min |
Temp. °C |
Temp. difference °C |
Hot air °C |
|
| 75 | 4 | 82 | 64 | -11 | 28 | 60 |
| 5 | 104 | 81 | -14 | 30 | 65 | |
| 6 | 120 | 93 | -16 | 32 | 66 | |
| 7 | 148 | 114 | -18 | 34 | 68 | |
| 50 | 4 | 87 | 44 | -13 | 30 | 35 |
| 5 | 110 | 55 | -16 | 32 | 43 | |
| 6 | 134 | 67 | -18 | 34 | 46 | |
| 7 | 157 | 89 | -20 | 36 | 49 | |
| 25 | 4 | 90 | 21 | -15 | 32 | 25 |
| 5 | 114 | 26 | -18 | 34 | 31 | |
| 6 | 138 | 32 | -20 | 36 | 35 | |
| 7 | 162 | 38 | -22 | 38 | 39 | |
SC-350
| Cold air ratio % |
Inlet air ( inlet air 16°C ) | Spit out cold air volume | Intake air / cold air | Hot air | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure kgf/cm² |
Air volume l/min |
Air volume l/min |
Temp. °C |
Temp. difference °C |
Hot air °C |
|
| 75 | 4 | 195 | 146 | -14 | 30 | 66 |
| 5 | 237 | 178 | -16 | 32 | 71 | |
| 6 | 283 | 212 | -19 | 35 | 76 | |
| 7 | 321 | 240 | -22 | 38 | 83 | |
| 50 | 4 | 208 | 113 | -22 | 38 | 55 |
| 5 | 249 | 124 | -24 | 40 | 58 | |
| 6 | 286 | 143 | -26 | 42 | 62 | |
| 7 | 339 | 169 | -28 | 44 | 68 | |
| 25 | 4 | 215 | 53 | -25 | 41 | 32 |
| 5 | 263 | 65 | -28 | 44 | 35 | |
| 6 | 311 | 78 | -31 | 47 | 39 | |
| 7 | 359 | 90 | -34 | 50 | 43 | |